Ever since CD/DVD drives have disappeared from most modern computers/laptops, knowing how to create a bootable USB flash drive has become an essential skill. Whether you’re installing a new operating system, running system recovery tools, or testing any OS build, it requires a bootable USB drive to load. While the process of creating a bootable USB in Windows is straightforward, many users are still unsure which method or tool to use.
A common concern is the safety of third-party utilities. Many such tools that are available online to make your USB bootable could be bundled with unwanted software, viruses, or malware. Although there are some tools that are very popular and quite reliable. However, if you don’t have those software utilities on your system, or you don’t want to install any tool. The good news is that you don’t actually need any external software at all to make a USB drive bootable.
Windows includes a powerful built-in utility called DiskPart that can help make your USB drive bootable in a few simple steps. It is fast, reliable, and eliminates the need to download any utility software. As long as you can access the command prompt in Windows, you are good to go.
In this guide, we’ll explore two methods to create a bootable USB drive: The first method uses DiskPart, and the second method uses an automated script that provides a one-click solution. Both methods will leave you with a clean bootable USB that’s ready to load any operating system or program of your choice.
Method 1: Create a Bootable USB in Windows with DiskPart(Command Prompt)
1. Open Command Prompt
Press Windows key + R, type “CMD” and press Enter.
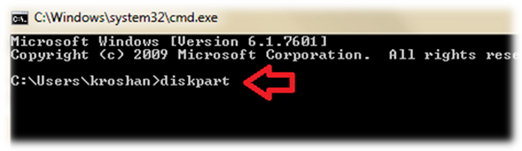
2. Launch DiskPart
In Command Prompt, type “Diskpart” and Press Enter.
(If a User Account Control prompt appears, click on the “Yes” button to allow)
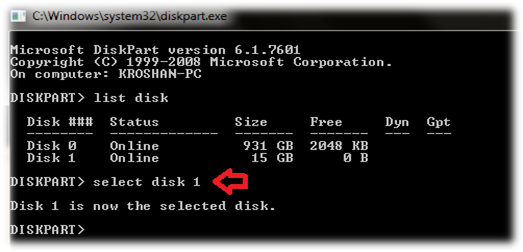
3. List all connected drives
This will display all Hard drives and USB drives that are connected to your system. You should also see your USB drive in the list, make a note of the Disk number of your USB Drive by identifying it by its size.
4. Select your USB drive
Type “select disk #”, replace # with your USB Drive’s disk number.
E.g.: Select Disk 1
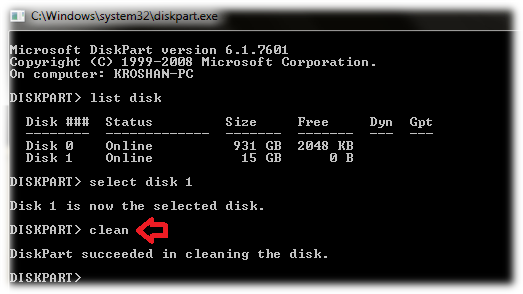
5. Clean the drive
Type “clean” and press Enter.
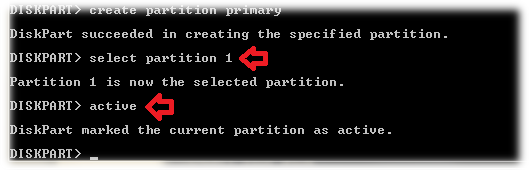
6. Create a primary partition
Type “create partition primary” and press Enter.
7. Select the partition and mark it active
Type “select partition 1” and once partition 1 is selected, type “active” and press Enter.
8. Format the drive to FAT32
Now type “format fs=fat32 quick” and press Enter. This will format your USB Drive in the FAT32 file system.
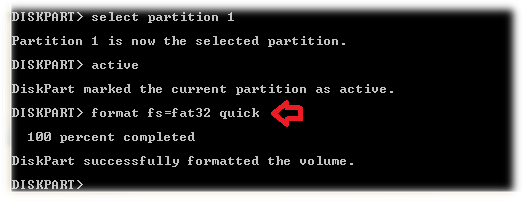
(Use ntfs instead of fat32, if your OS files are larger than 4 GB)
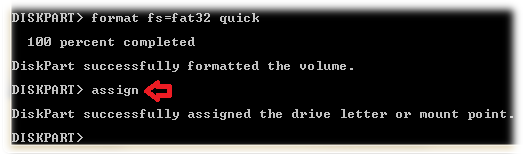
9. Assign a drive letter
On successfully completing the format, Type “assign” to give your USB drive a letter.
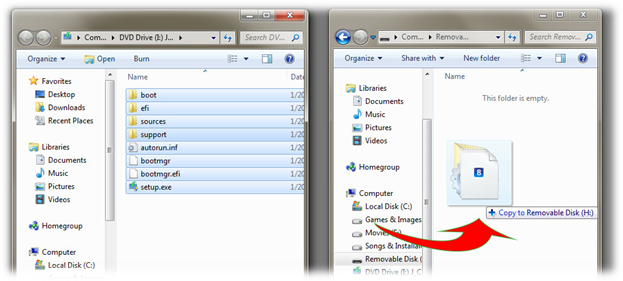
10. Copy your OS/Program files
Your USB drive is now bootable, but empty. Copy the full contents of your operating system installation files onto the USB drive.
Your bootable USB is now ready to use. Make sure to set your BIOS/UEFI to boot from USB, and you’re good to go.
You are now all set to boot your OS using your USB Drive.
Method 2: Create a Bootable USB in Windows with a DiskPart Script
If you prefer to skip the manual steps, you can automate them with a simple script. This script will automatically run all the above commands for you.
1. Download the file USB Bootable Script. Extract and run the file.

2. Enter the Disk Number of your USB drive when prompted.
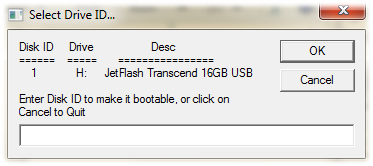
3. Copy your OS/program files to the USB drive once the script finishes.
Important Note: Always double-check the disk number before running DiskPart commands. Choosing the wrong disk could erase your data on that drive.


